All You Need to Know about PCIe
Posted on July 13, 2021
What does PCIe stand for?
Peripheral Component Interconnect Express or PCIe is one of the central connectivity technologies of a computer. It helps expand the capabilities of a PC and is an essential feature for any computing system, industrial or otherwise.
But at the same time, not many people actually know much about this standard. Compared to the more ubiquitous USB, PCle is still somewhat unknown. What exactly is PCIe? What does it do? And do all those generations change anything? This article will answer all these questions.
What is PCIe?
In a way, PCIe is similar to the USB standard. Just like the Universal Serial Bus enables devices to communicate with the computer, the PCI express lets peripheral components interface with the computer. But what then is the difference between them?
Speed. USB connections can only support things like data transfer and input devices – its transfer rate is too low for anything more complex. With the PCI-e though, high-performance components can be integrated directly into the motherboard.
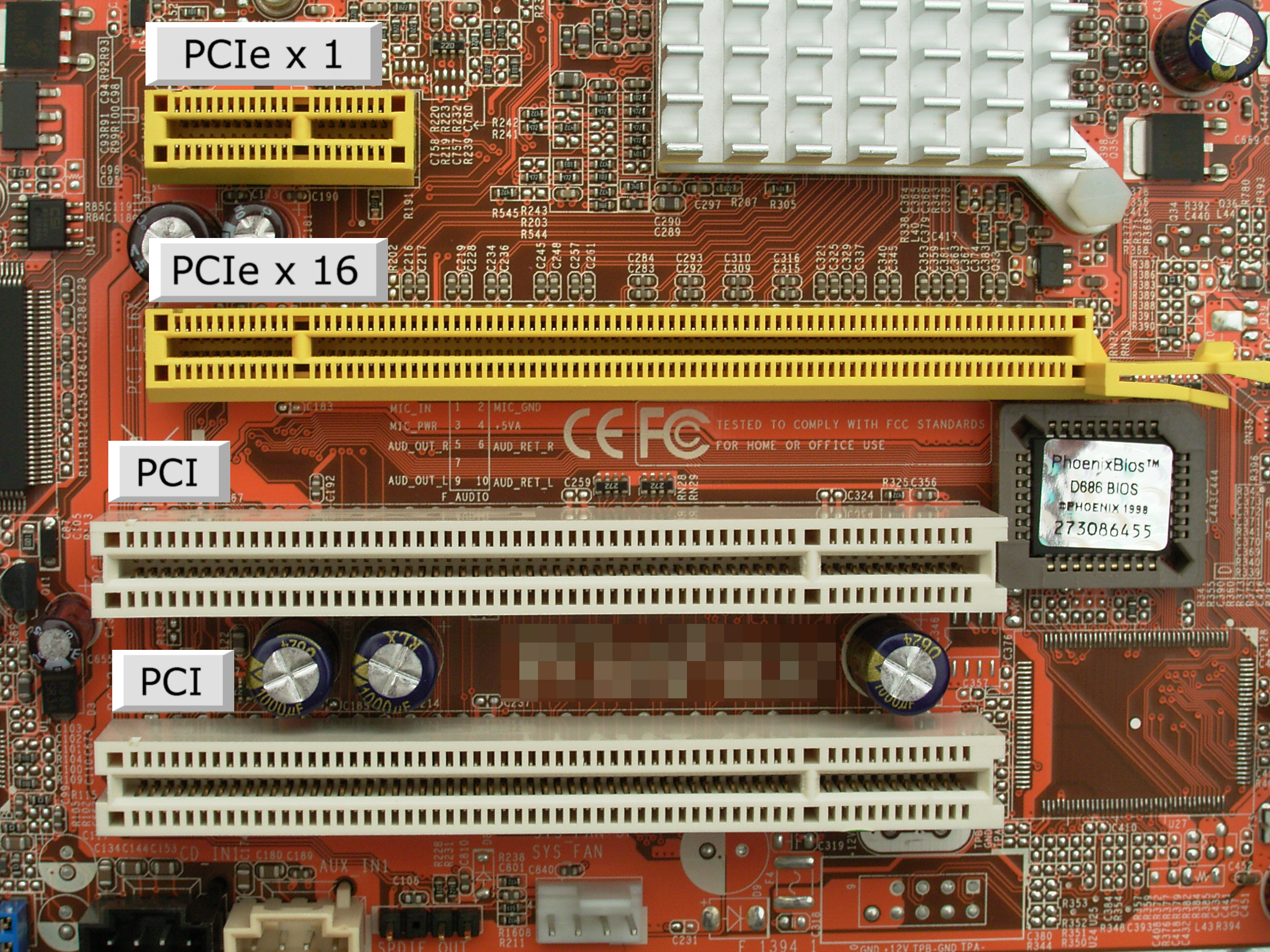
Graphic cards, network cards (both Wi-Fi and Ethernet), sound cards, SSDs, and many other expansion cards are connected through PCIe. Not all of these use the exact same configuration, though. PCIe slots have a number of ‘lanes’, which decide how much data they can carry at once. Data-intensive additions like graphic cards must use the highest number of lanes (x16), while other applications might use fewer.
Why is PCIe important?
Most of the really important components of a computer make use of this standard. Need high-speed Wi-Fi on your system? PCIe. Want to install a discrete GPU? You need PCIe. Wish to install an SSD? PCIe again.
Without enough PCIe slots on your embedded PC, you will be losing out on many important upgrades. Most industrial applications today need at least a high-speed ethernet connection, if not Solid State Drives.
Applications are increasingly making use of AI-based algorithms as well, which require discrete GPUs for their parallel processing needs. Then there are distributed applications like IoT or surveillance systems, where a Wi-Fi card is often needed.
What are the form factors for PCIe?
PCI express is mostly divided by the number of lanes a slot has. This goes from the most basic x1 to x2, x4, x8, and all the way up to x16. Each additional lane is another path for the transmission of data, exponentially increasing the transfer speed.
But what does this mean for the cards meant to be installed into these slots? Do their sizes differ? Or can you insert any peripheral into any type of PCIe slot?
Well, it depends. An increased number of lanes usually translates to a larger slot. So a card that needs PCIe x16 cannot fit into a slot with fewer lanes. But a smaller card can easily use a larger slot. This means that if a motherboard has a PCIe x16 slot, it can be used to install an expansion card, no matter its form factor.
A note about modes
Sometimes you will come across a PCIe slot with a different mode. For example PCIe x16 @ x4. What this means is that while the slot can physically accommodate cards up to x16, the performance will actually only use 4 lanes.
This is a common practice in most motherboards that lack the hardware capability for a faster transfer speed. As a result, any PCI express card can be installed on such a motherboard, even if it may not perform at its full speed.
Do the PCIe generations matter?
The very point of PCIe is to transfer large amounts of data quickly and efficiently. Every subsequent generation of the standard makes it better at doing so.
The bandwidth has gone up from 2.5 GT/s to a whopping 32 GT/s, with the transfer speeds coming to 63 Gb/s in the currently used 5th generation. A version 6.0 is already in the works, expected to double both of these rates and give an incredible boost to the standard.
Conclusion
PCI Express is one of the hidden features to look out for when choosing an embedded computer. And while you can always add more USB slots using USB hub attachments and whatnot, similar extensibility is not possible with the PCIe.
You must decide what expansion cards you intend to install and choose a motherboard accordingly. Attention must also be paid to the number of lanes available, and the version of the standard in use.
So the next time you are shopping for a major system upgrade, keep an eye on the PCIe slots. Try to get the best possible configuration so that it can excel in every application.
